NUMBER SYSTEMS
NUMBER SYSTEMS
In Hindu Arabic System, we use ten symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 called digits to represent any number. This is
the decimal system where we use the numbers 0 to 9. 0 is called insignificant digit.
A group of figures, denoting a number is called a numeral. For a given numeral, we start from extreme right
as Unit’s place, Ten’s place, Hundred’s place and so on.
We represent the number 309872546 as shown below:
6-units
4-Tens
5-Hundreds
2-Tounsands
7-Ten thousand
8-Lacs
9-Ten lacs(million)
0-Crocres
3-Ten croces
We read it as
“Thirty crores, ninety- eight lacs, seventy-two thousands five hundred and forty-six.”
In this numeral:
The place value of 6 is 6 ×1 = 6
The place value of 4 is 4 ×10 = 40
The place value of 5 is 5 ×100 = 500
The place value of 2 is2 ×1000 = 2000 and so on.
The face value of a digit in a numbers is the value itself wherever it may be.
Thus, the face value of 7 in the above numeral is 7. The face value of 6 in the above numeral is 6 and in the above
numeral is 6 and so on.
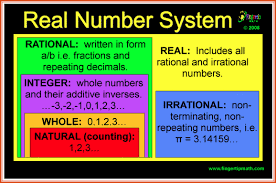
Natural numbers:
Counting numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,... are know as natural numbers.
The set of all natural numbers, can be represented by
N= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5,….}
Whole numbers
If we include 0 among the natural numbers, then the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … are called whole numbers.
The set of whole number can be represented by
W= {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5…}
Clearly, every natural number is a whole number but 0 is a whole number which is not a natural number.
INTEGERS
All counting numbers and their negatives including zero are know as integers.
The set of integers can be represented by
Z or I = {…-4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}
Positive Integers
The set I+ ={1, 2, 3, 4,…} is the set of all positive integers. Clearly, positive integers and natural numbers are synonyms.
Negative Integers:
The set I- = {-1, -2, -3…} is the set of all negative integers. 0 is neither positive nor negative.
Non-negative Integers
The set {0, 1, 2, 3,…} is the set all non-negative integers.
Rational Numbers
The numbers of the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0, are known as rational numbers, e.g. 4/7, 3/2, -5
/8, 0/1, -2/3, etc.
The set of all rational numbers is denoted by Q. i.e. Q ={x:x =p/q; p,q belong to I, q≠0}.
Since every natural number ‘a’ can be written as a/1, every natural number is a rational number. Since 0 can
be written as 0/1 and every non-zero integer ‘a’ can be written as a/1, every integer is a rational number.
Every rational number has a peculiar characteristic that when expressed in decimal form is expressible
rather in terminating decimals or in non-terminating repeating decimals.
For example, 1/5 =0.2, 1/3 = 0.333…22/7 = 3.1428704287, 8/44 = 0.181818…., etc.
The recurring decimals have been given a short notation as
0.333…. = 0.`3
4.1555… = 4.0`5
0.323232…= 0.`32.
Irrational Numbers:
Those numbers which when expressed in decimal from are neither terminating nor repeating decimals are known as
irrational number, e.g. √2, √3, √5, π, etc.
Note that the exact value of p is not 22/7. 22/7 is rational while π irrational number. 22/7 is approximate value of π.
Similarly, 3.14 is not an exact value of it.
Real Numbers
The rational and irrational numbers combined together are called real numbers, e.g.13/21, 2/5, -3/7, Ö3, 4 + Ö2, etc.
are real numbers.
The set of all real numbers is denote by R.
Note that the sum, difference or product of a rational and irrational number is irrational, e.g. 3+ √2, 4-√3,
2/3-√5, 4√3, -7√5 are all irrational.
Even Numbers
All those numbers which are exactly divisible by 2 are called even numbers, e.g.2, 6, 8, 10, etc., are even numbers.
Odd Numbers
All those numbers which are not exactly divisible by 2 are called odd numbers, e.g. 1, 3, 5, 7 etc., are odd numbers.
Prime Numbers
A natural number other than 1 is a prime number if it is divisible by 1 and itself only.
For example, each of the numbers 2, 3, 5, 7 etc., are prime numbers.
Composite Numbers
Natural numbers greater than 1 which are not prime, are known as composite numbers.
For example, each of the numbers 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, etc., are composite numbers.
Note:
1. The number 1 is neither a prime number nor composite number.
2. 2 is the only even number which is prime
3. Prime numbers up to 100 are:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19,23, 29, 31, 37, 41,43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, i.e. 25 prime
numbers between 1 and 100.
4. two numbers which have only 1 as the common factor are called co-primes or relatively prime to each
other, e.g. 3 and 5 are co-primes.
Note that the numbers which are relatively prime need not necessarily be prime numbers, e.g. 16 and 17 are
relatively prime although 16 is not a prime number.


Comments
Post a Comment